This page contains notes about the usual stack frame layout (calling convention) on ARM processors.
Most information is taken from ARM procedure calling conventions and recursion .
The conventions are defined by ARM and are called PCSAA.
| Link Register | Contains the return address of an function call |
| Caller | Code that calles a function |
| Callee | Function that is called by other code |
| Frame Pointer | Points to the actual stack frame (Base Pointer on x86) |
| Stack Pointer | Points always to the top of the stack |
General Notes
BLandBLXuseR14(RL) as link register- Simple functions (i.e. leaf functions) use
MOV PC, LRto return to the caller function R0-R3are used to pass arguments to the callee (can be overwritten by callee, caller saved)R0contains often the resultR4-R10must be saved by the called function (callee) if needed- They must be unchanged after return
- Callee saved
- Restore before return
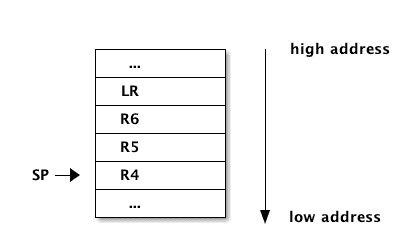
R13(SP) contains the address of top of the stack (last filled poition)- Stack is Full-Descending:
SPpoints to the last filled location- Stack grows downwards (from higher to lower addresses)
PUSH/POP: STMFD/LDMFD (Store multiple Full-Descent, Load multiple Full-Descent)
LDMFD SP, {R0-R3}is equvalent to:
LDR R0, [SP]
LDR R1, [SP, #4]
LDR R2, [SP, #8]
LDR R3, [SP, #12]To alter (update) SP:
LDMFD SP!, {R0-R3}LR needs to be saved on stack for non-leaf functions
_func:
STMFD SP!, {R4-R6, LR}
; ... code of func
LDMFD SP!, {R4-R6, PC} ; Pushing stacked LR directly to PC => return to caller- The order of registers in
STMFDandLDMFDis always the same: lower regisers at lower addresses
- More general stack frame:
- Quick clear down of stack frame:
MOV SP, FP